Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
Valutech sells a variety of shell and tube heat exchangers using computer generated thermal and mechanical design, seismic analysis and detailed, scaled manufacturing drawings.

Each heat transfer device is individually designed to ensure optimum compatibility with its application. Valutech represents Doyle and Roth, Enerquip and other manufacturers product designs and builds:
Condensate coolers
High temperature hot water steam generators
Liquid chillers
Chemical process equipment
Vapor and steam condensers
Material:
The demands made today on manufacturers by the diverse processes that use heat exchangers require an equally diverse range of construction materials and the ability to work with them with full competency. Our products are carbon steel, stainless, titanium and nickel or copper alloys. Every unit is manufactured under strictly controlled standards of workmanship, ensuring conformity with ASME Code Section VIII Div 1.
Capabilities
- Computer Generated Thermal and Mechanical Design
- Computer Generated Seismic Analysis
- Computer Generated Drawings, Detailed and Scaled
- NC/CNC Drilling
- Custom Fabrication
Codes and Standards
- ASME
- TEMA
- HEI
- API
- Coast Guard
Materials of Construction
- Carbon Steel
- Cast Iron
- Stainless Steel
- Brass
- Copper
- Cupro-Nickel
- Hastelloy
- Alloy 20
- Titanium
- Inconel
- Incolloy
- Monel
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger Cleaning
Checkout all Heat Exchangers
About Shell and Tube Heat Exchangers
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs.[1][2] It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell (a large pressure vessel) with a bundle of tubes inside it. One fluid runs through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes (through the shell) to transfer heat between the two fluids. The set of tubes is called a tube bundle, and may be composed of several types of tubes: plain, longitudinally finned, etc.
Two fluids, of different starting temperatures, flow through the heat exchanger. One flows through the tubes (the tube side) and the other flows outside the tubes but inside the shell (the shell side). Heat is transferred from one fluid to the other through the tube walls, either from tube side to shell side or vice versa. The fluids can be either liquids or gases on either the shell or the tube side. In order to transfer heat efficiently, a large heat transfer area should be used, leading to the use of many tubes. In this way, waste heat can be put to use. This is an efficient way to conserve energy.
Heat exchangers with only one phase (liquid or gas) on each side can be called one-phase or single-phase heat exchangers. Two-phase heat exchangers can be used to heat a liquid to boil it into a gas (vapor), sometimes called boilers, or cool a vapor to condense it into a liquid (called condensers), with the phase change usually occurring on the shell side. Boilers in steam engine locomotives are typically large, usually cylindrically-shaped shell-and-tube heat exchangers. In large power plants with steam-driven turbines, shell-and-tube surface condensers are used to condense the exhaust steam exiting the turbine into condensate water which is recycled back to be turned into steam in the steam generator. to change this text.
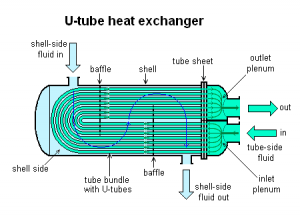
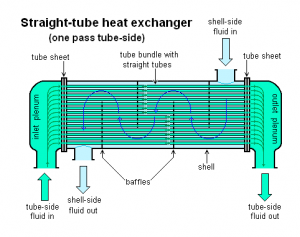
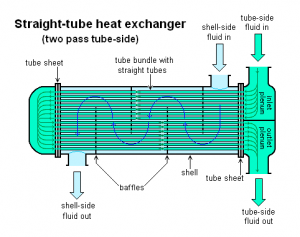
There are often baffles directing flow through the shell side so the fluid does not take a short cut through the shell side leaving ineffective low flow volumes. These are generally attached to the tube bundle rather than the shell in order that the bundle is still removable for maintenance.
Counter current heat exchangers are most efficient because they allow the highest log mean temperature difference between the hot and cold streams. Many companies however do not use two pass heat exchangers with a u-tube because they can break easily in addition to being more expensive to build. Often multiple heat exchangers can be used to simulate the counter current flow of a single large exchanger.
Selection of tube material
To be able to transfer heat well, the tube material should have good thermal conductivity. Because heat is transferred from a hot to a cold side through the tubes, there is a temperature difference through the width of the tubes. Because of the tendency of the tube material to thermally expand differently at various temperatures, thermal stresses occur during operation. This is in addition to any stress from high pressures from the fluids themselves. The tube material also should be compatible with both the shell and tube side fluids for long periods under the operating conditions (temperatures, pressures, pH, etc.) to minimize deterioration such as corrosion. All of these requirements call for careful selection of strong, thermally-conductive, corrosion-resistant, high quality tube materials, typically metals, including aluminium, copper alloy, stainless steel, carbon steel, non-ferrous copper alloy, Inconel, nickel, Hastelloy and titanium.[3] Fluoropolymers such as Perfluoroalkoxy alkane (PFA) and Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) are also used to produce the tubing material due to their high resistance to extreme temperatures.[4] Poor choice of tube material could result in a leak through a tube between the shell and tube sides causing fluid cross-contamination and possibly loss of pressure.
Applications and uses
The simple design of a shell and tube heat exchanger makes it an ideal cooling solution for a wide variety of applications. One of the most common applications is the cooling of hydraulic fluid and oil in engines, transmissions and hydraulic power packs. With the right choice of materials they can also be used to cool or heat other mediums, such as swimming pool water or charge air.[5] One of the big advantages of using a shell and tube heat exchanger is that they are often easy to service, particularly with models where a floating tube bundle (where the tube plates are not welded to the outer shell) is available.[6]
All welders are ASME, AWS and API Qualified with the ability to weld Carbon, Low and High Alloy Steels, Nickel, Nickel Alloys, Copper Alloys, Chrome-Moly, Hastelloy, Incoloy, Inconel, Duplex and all grades of Stainless Steel among other specialties. Our shop has the equipment and expertise in the following welding methods:
Welding Ability
- Gas Metal Arc (GMAW) MIG
- Gas Tungsten Arc (GTAW) TIG
- Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) FCA
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW)
- Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) Stick
- Weld Overlay
Machining, shearing and rolling

Our craftsman have an average of 20 years experience in the precision fabrication of custom body flanges, tubesheets, baffles and miscellaneous components up to 84″ in diameter.
Cylinders above 24″ for Carbon Steel and above 12″ for Alloys up to 1 1/4″ thickness x 18′ in length are rolled in-house. We have the ability to shear and bend plates up to 1/2″ thick.
Machining & Rolling Equipment
- Horizontal Lathes (up to 84″)
- Rollers (up to 1 1/4″ thick)
- 300 Ton Capacity Hydraulic Brake and Shear
- Automatic Manipulators & Positioners
Drilling

Our manufacturers use high precision automated machinery, capable of drilling deep holes to an extremely high tolerance. Tubesheets, baffles and flanges are drilled using our CNC equipment for accuracy and speed. Our shop engineers program the equipment directly from the fabrication CAD drawings. Qualified machinists then set the piece in place and monitor the drilling process.
Drilling Equipment
- Radial Drills (up to 5′ arm, 13′ column)
- Dual Spindle N/C Gun Drill (90″x90″x20″ depth)
- Vertical Boring Mill (up to 84″ dia)
Tube Bending

We have the in-house capability to bend tubes for “U” Bundles. Our machinery and operators are skilled at bending all tube grades and sizes to a specified radius while taking into consideration reduction in tube wall thickness.
Assembly

All components are fabricated and assembled in the same location for improved efficiency. Our assemblers have experience with all TEMA pressure vessel types including fixed tubesheet, floating tubesheet and U-Tube exchangers
Assembly Space
- 70′ x 230′ Bay with 28′ Under Hook
- 70′ x 190′ Bay with 12′ Under Hook
- 40′ x 110′ Bay with 45′ Under Hook
Thermal Rating

All Thermal design is performed by our in-house Process Engineers, utilizing Aspen Tech Thermal Rating software and custom developed programming. We operate with the understanding that correct and thorough input is required for accurate results. Our engineers dictate the design based on experience and knowledge of thermal properties, using the software only as tool.
We have the capability to design all major industrial shell and tube heat exchanger equipment, including single phase, multi phase, condensers, evaporators and specialty units. We can provide complete thermal design, rating or review your calculations to offer value engineering solutions.
Mechanical Design
Our engineers are experts in the design and mechanical optimization of heat transfer equipment. We have a thorough understanding of all applicable codes and design references including ASME, TEMA, API 660, PIP and are well versed in the interpretation of customer specifications.
Our manufacturers have always been at the cutting edge of the adoption of the latest mechanical design software. At the early stages, we worked hand in hand with developers to provide input with regard to industry standards calculations and output format. This has helped to optimize the software still being used today.
We continue to use the Aspen Mechanical Suite which draws on the long heritage of the B-JAC Teams software to optimize design by recognizing the interaction of key components. This in conjunction with our in-house custom programmed mechanical software provides us with the ability to minimize material usage, resulting in an efficient, cost effective design of shell and tube heat exchangers.
3D Rendering Design Capability
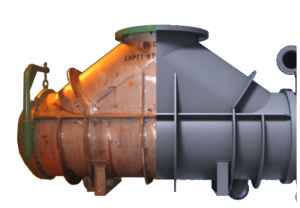
The design and fabrication of highly complicated shell and tube heat exchangers and pressure vessels are streamlined with the use of 3D design software. This method reduces both schedule and cost by accurately dimensioning components with challenging geometric features and verifying clearances prior to the start of fabrication. The customer also benefits from the use of this model when creating piping plans and determining the special requirements of their plant.
Valutech also offers the following
- Replacement tube bundles
- Intercoolers and aftercoolers
- Pressure vessels
- Steam generators
- Chillers / Condensers

